Websphere Basics
Basic Definitions:
WebSphere architectures contain one or more computer systems, which are referred to in WebSphere terminology as nodes. Nodes exist within a WebSphere cell. A WebSphere cell can contain one node on which all software components are installed or multiple nodes on which the software components are distributed.
A typical WebSphere cell contains software components that may be installed on one node or distributed over multiple nodes for scalability and reliability purposes. These include the following:
- A Web server that provides HTTP services
- A database server for storing application data
- WebSphere Application Server (WAS) V5
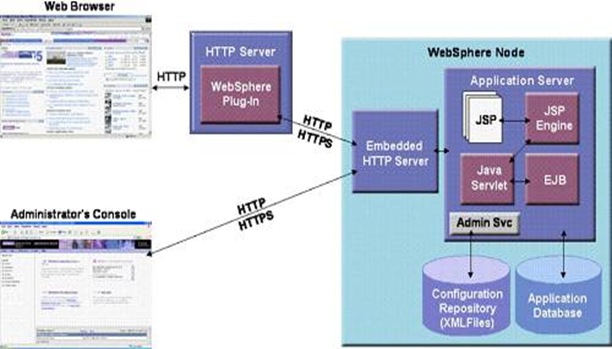
HTTP server
The HTTP server, more typically known as the Web server, accepts page requests from Web browsers and returns Web page content to Web browsers using the HTTP protocol. Requests for Java servlets and JavaServer Pages (JSPs) are passed by the Web server to WebSphere for execution. WebSphere executes the servlet or JSP and returns the response to the Web server, which in turn forwards the response to the Web browser for display.
WebSphere V5 supports numerous Web servers such as Apache, Microsoft IIS, Netscape and Domino. However, WebSphere has the tightest integration with Domino because IBM provides single sign-on capabilities between WebSphere and Domino.
WebSphere plug-in
The WebSphere plug-in integrates with the HTTP Server and directs requests for WebSphere resources (servlets, JSPs, etc.) to the embedded HTTP server (see below). The WebSphere plug-in uses a configuration file called plugin-cfg.xml file to determine which requests are to be handled by WebSphere. As applications are deployed to the WebSphere configuration, this file must be regenerated (typically using the Administration Console) and distributed to all Web servers, so that they know which URL requests to direct to WebSphere. This is one of the few manual processes that a WebSphere administrator must do to maintain the WebSphere environment.
Application server
The application server provides a run-time environment for J2EE applications (supporting servlets, JSPs, Enterprise JavaBeans, etc.). A node can have one or more application server processes. Each application server runs in its own runtime environment called a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The JVM provides complete isolation (crash protection) for individual applications servers.
Application database
WebSphere applications such as IBM’s commerce and portal products, as well as applications you create yourself, use a relational database for storing configuration information and data. WebSphere V5 ships with the Cloudscape database and supports a wide range of database product, including the following:
- IBM DB2
- Informix
- Oracle
- SQL Server
- Sybase
Administration console
The administration console provides a Web-based interface for managing a WebSphere cell from a central location. The administration console can be used to change the configuration of any node within the cell at run-time. Configuration changes are automatically distributed to other nodes in the cell.
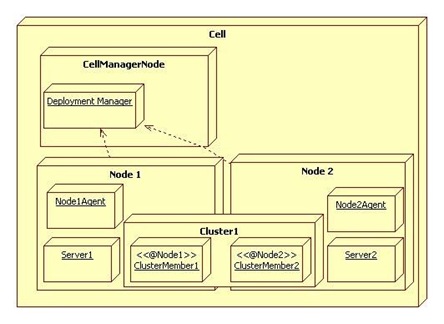
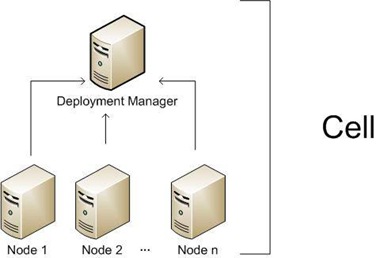
Cell:
A Cell is a virtual unit that is built of a Deployment Manager and one or more nodes.
The Deployment Manager is a process (in fact it is an special WebSphere instance) responsible for managing the installation and maintenance of Applications, Connection Pools and other resources related to a J2EE environment. It is also responsible for centralizing user repositories for application and also for WebSphere authentication and authorization.
The Deployment Manager communicates with the Nodes through another special WebSphere process, the Node Agent.
The Node is another virtual unit that is built of a Node Agent and one or more Server instances.
The Node Agent it the process responsible for spawning and killing server processes and also responsible for configuration synchronization between the Deployment Manager and the Node. Extra care must be taken when changing security configurations for the cell, since communication between Deployment Manager and Node Agent is ciphered and secured when security is enabled, Node Agent needs to have configuration fully resynchronized when impacting changes are made to Cell security configuration.
Servers are regular Java process responsible for serving J2EE requests (eg.: serving JSP/JSF pages, serving EJB calls, consuming JMS queues, etc).
Clusters
And to finish, Clusters are also virtual units that groups Servers so resources added to the Cluster are propagated to every Server that makes up the cluster, this will in fact affect usually more than a single Node instance.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.